Consortium of Bryophyte Herbaria
- building a Consortium of Bryophytes and Lichens as keystones of cryptobiotic communities -
|
|
|
|
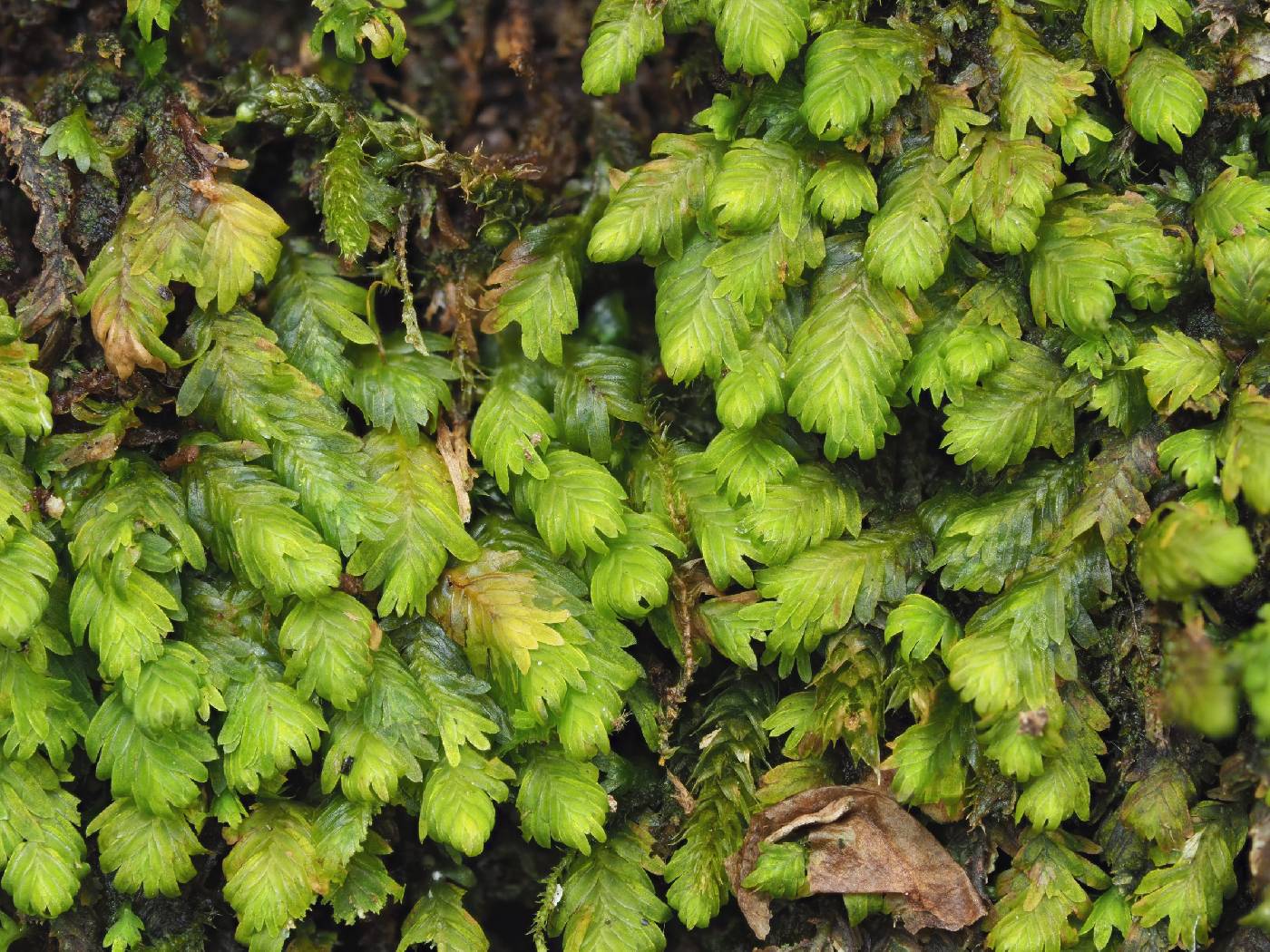
Family: Fissidentaceae
fissidens moss
[Dicranum subbasilare D. Mohr, more] |
|
Powered by Symbiota.